Roofing contractors often are amazed at the time-tested craftsmanship of sheet-metal systems that are removed from historical structures. It's not uncommon for some of these systems to date to World War II. The one thing all long-lasting systems such as standing-seam, flat-lock and built-in gutters have in common is their ability to accommodate thermal movement. Unfortunately, when thermal movement is restricted, contractors may witness failures in as little as five years.
If you install metal roof systems on residential structures, it's important to understand the direction and effect of thermal movement on various metal types.
The basics
The principles of thermal movement can easily be misunderstood because anything that is not visible to the naked eye can be overlooked. For example, it's not likely for a roofing contractor to notice a 1/4-inch expansion in an aluminum panel. In addition, failures caused by thermal movement usually occur over dozens of thermal cycles or seasons, and the original installers or designers sometimes are not around to witness the failures. For that matter, a homeowner or building owner could have sold the property. In addition, failures associated with thermal movement often are misdiagnosed and blame is placed upon poor workmanship or improper soldering.
When thinking about thermal movement, it helps to visualize the movement of liquid mercury in an old-fashioned thermometer. As temperature rises, the atomic particles in the mercury move faster, causing it to expand. Conversely, as the temperature lowers, the atomic particles slow down and the liquid metal contracts.
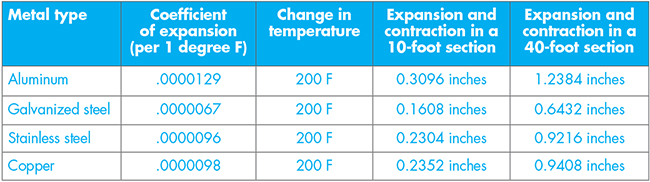
Figure 1: A comparison of metals and their reactions to thermal movement |
The rate of thermal movement varies by the type of metal installed and temperature of the base metal. It is important to note ambient air temperature will differ from the temperature of the metal, and direct solar radiation plays a major role in this process. Also, the surface temperature of metal roofing materials can range from 25 degrees Fahrenheit cooler than ambient air temperatures in the winter and more than 100 degrees Fahrenheit warmer than ambient air temperatures in direct summer sunlight. Based on these temperatures, a base metal could have a temperature change of more than 200 degrees Fahrenheit.
The formula Delta L = L•Delta T•Ce where Delta L is the change in length, Delta T is the change in temperature and Ce is the coefficient of expansion for each metal can provide the amount of expansion and contraction in common roofing materials (see Figure 1).
The coefficient of expansion is constant for all metal thicknesses. For example, 24-gauge galvanized steel has the same coefficient of expansion as 26-gauge galvanized steel, and the coefficient of expansion for 16-ounce copper is the same as that of 20-ounce copper.
Flat-lock roof systems
Flat-lock roof systems are designed to absorb thermal movement within each panel. Proper design includes maximum panel lengths of 18 by 24 inches for copper and stainless steel; galvanized steel pans can be slightly larger. Thermal movement is absorbed in these systems when installers lock panels onto hook strips on the roof's perimeter and connect them with a flat seam in the roof's field. All panels are secured to the roof system using cleats installed 12 inches on center with two fasteners in each cleat. The panels must be fully sweated with solder in all low-slope applications.
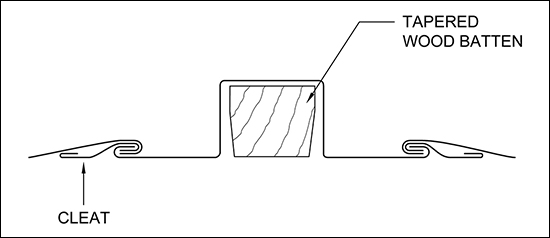
Figure 2: A common expansion detail using tapered wood batten |
Solder joints are the weakest parts of the system as they usually consist of equal parts lead and tin. The melting point of solder is around 390 F, and the melting points of copper and galvanized steel are 1,981 F and 2,500 F, respectively. Failures in the solder joints can occur from expansion and contraction of the substrate or building structure. For this reason, expansion joints should be installed on flat-lock systems with lengths greater than 30 feet in any direction. A common expansion detail using a tapered wood batten can be seen in Figure 2.
If the panels are similar in size and temperature, forces from expansion and contraction will be equally absorbed within the cleats located at the seams. Design professionals and installers can control panel size but not panel temperature. Direct solar radiation (or lack thereof) can vary throughout a roof and affect the rate of expansion differently from one panel to another, especially on larger roofs. As the surface area of each panel increases, the force and length of thermal movement increases. Smaller panels are able to absorb thermal movement better than larger panels. It is imperative to avoid copper or stainless-steel panels larger than 18 by 24 inches because thermal movement in larger panels have greater force, which increases stress on soldered flat-lock seams. Common failures from thermal movement in flat-lock systems occur when the perimeter is improperly attached to another metal system, such as built-in gutters or wall flashings.
It is important to note copper, which already has a higher coefficient of expansion, absorbs more heat than other metals. This increases its surface temperature and the associated thermal movement. Galvanized metal systems that are painted can reflect sunlight, decreasing their surface temperatures. Failures can occur when removing a more reflective galvanized steel or terne metal system and duplicating the details using copper.
Built-in gutter systems
Built-in gutter liners must consist of a solderable metal such as galvanized steel, stainless steel or copper. As detailed in Figure 1, the thermal movement of galvanized steel systems is much less than that of copper and stainless-steel liners. Homeowners often choose more expensive copper liners for aesthetic reasons only to witness failures because of increased stress from the higher coefficient of thermal expansion. Although steel liners are susceptible to corrosion if they are not properly maintained (painted), they are less likely to fail from restricted movement on most residential projects.
Major damage can occur when built-in gutter systems fail because they are part of a building's structure. Common failures roofing contractors encounter are caused by leaks in the seams and deterioration of the metal liner. Seam failures often can be prevented by the proper accommodation of thermal movement in the system. The seams are the liner's weakest points, similar to the seams in flat-lock systems.
When using the formula provided for gutter systems, it's important to understand the movement of the liner at the width and length. A common steep-slope built-in gutter liner is fabricated in 10-foot lengths and 28-inch widths. The change in the width is minimal on most residential applications. If "stretch outs," or widths, of the gutters are longer than normal, consider using thicker metal, such as 24-ounce copper or 24-gauge galvanized steel.
The expansion and contraction of a gutter liner will occur in a more significant manner along the length. The change in length on a 10-foot section of copper is nearly 1/4 of an inch based upon a temperature change of 200 degrees. When four 10-foot sections of copper gutters are lapped and riveted at the seams, the accumulation of thermal movement can result in a change in length of nearly 1 inch. A 200-degree temperature differential is not out of the realm of possibility when a metal liner is exposed to direct solar radiation.
Proper accommodation for thermal movement in a gutter system should start with a continuous hook strip on the gutter's face. It also should include cleats to secure the gutter apron (beneath the roofing material) to the roof sheathing. These two securement methods will allow the liner to float along its length.
Installers also can place expansion joints at appropriate locations. If two outlets or fixed points exist on the ends of the same linear section, the expansion joint should be placed in the middle of the gutter as the movement would occur away from each fixed point. If one outlet is located at the end of the gutter, a single expansion joint would be installed on the opposite end of the outlet tube. An expansion joint should be installed on all sections longer than 30 feet.
Installation practices that can restrict movement in a built-in gutter include the following:
- Fastening directly through the metal liner on the face of the gutter
- Securing the gutter apron directly to the roof deck with fasteners liner
- Rivets at the seams that penetrate the wood substrate
The force of thermal movement along the length of a built-in gutter liner usually is no match for a rivet that penetrates a wood substrate. Rivets often can be found bent sideways at seams, causing the solder to fracture. Carefully drilled holes through the wood substrate can allow the rivets to move with the liner and not damage the seams.
When movement is restricted, stress fractures can occur in the liner's field. Similar to an aluminum soda can that is bent back and forth several times, a puncture eventually will develop. Forces from thermal movement exerted on gutter liners at imperfections from the installation or fabrication eventually can rupture if the movement is great enough.
It is important to note the exposure of the gutter liner to solar radiation will vary on different sides of a house. Failures from thermal movement occur on the southern exposure more often than any other direction.
Difficult repair work
It is important to understand and accommodate thermal movement before installing any metal roofing project because repairs after installation rarely are effective. Resoldering a seam is nearly impossible after the base metal has oxidized or is exposed to dirt and debris. Elastomeric coatings and roof cement are temporary solutions to stopping leaks on these systems. Without accommodating thermal movement, coatings and cement are subject to the same forces that caused the seams to fail in the first place. Furthermore, expansion joints, hook strips and cleats are difficult and costly to add to an existing liner or flat-lock roof. Complete system replacement usually is the only long-term option when these systems fail.
Standing-seam roof systems
Raised seams provide additional strength to metal panels and accommodate thermal movement. Standing-seam systems are attached with clips to allow panels to expand and contract vertically. Similar to built-in gutter systems, expansion along the width of each panel is not large enough to be a cause for concern. Individual panels absorb horizontal movement across the roof surface.
An exposed fastener at the ridge, eave or midpoint that secures a panel to the substrate is a fixed point. Fixed points are required on standing-seam systems to eliminate drag forces. If panels are installed without fixed points, the panels can slide vertically toward the eaves. Thermal movement will occur away from a fixed point as follows:
- Fixed point located at ridge: movement occurs toward the eave
- Fixed point located at eave: movement occurs toward the ridge
- Fixed point at the midpoint: movement is directed away from the fastener toward the roof eave and ridge
Note that multiple fixed points can cause panels to buckle. It is common to see multiple fixed points near penetrations. The panels at these locations will be negatively affected by the restriction of thermal movement. If the panel length is long enough, stress caused by movement toward an exposed fastener can allow water infiltration. In these situations, it is important to ensure the panels can float in one direction even where penetrations exist.
Underlayment considerations
When designing any metal roof or gutter system, it is important to realize not all types of underlayment are acceptable. Granule-surfaced underlayment, like sandpaper, is abrasive to sheet metal as it expands and contracts. Also, an underlayment with a low melting point such as asphalt can stick to metal panels and tear during thermal movement. For this reason, it is important to apply underlayment that is suitable for high temperatures in metal systems. Rosin paper can be used as a slip sheet between metal panels and underlayment. Because seams are soldered using a 400 F iron, rosin paper also prevents asphalt underlayment from melting and contaminating the seams.
Underlayment also can be used to protect the underside of metal systems from interior moisture that could corrode the panels.
Know the facts
Failures are more likely to occur when materials with high coefficients of thermal expansion, such as aluminum, copper and stainless steel, are improperly installed. Systems that were installed decades ago with terne metal or painted steel will not have the same physical properties as a system designed with a different type of metal panel or liner.
Copper is known for its beauty and endurance, but it absorbs heat and expands at a greater rate than other metals. Homeowners who request materials with greater thermal movement also should receive the accessories that secure the panels without restricting movement, including cleats, expansion joints, panel clips and hook strips.
For more information, reference the Metal Panel section in The NRCA Roofing Manual: Metal Panel and SPF Roof Systems—2016 and Copper and Common Sense by Revere Copper, Rome, N.Y.
Nick Sabino is president of Deer Park Roofing Inc., Cincinnati.
Three reasons to not remove built-in gutter liners
Gutter companies often recommend removing built-in gutter systems in favor of less expensive aluminum hanging gutters. But there are three architectural concerns with removing the overhang that contains built-in gutter liners:
- The overhang shades the walls of the house in summer when the sun is high in the sky. During winter, the sun is low in the sky, and solar radiation on the walls of the house has a positive effect on thermal performance.
- Water infiltration can occur in the windows or siding.
- Leaks can occur at the home's foundation.
Definitions
- Absorption of thermal movement occurs in flat-lock metal systems and across standing-seam panels. The movement is contained in each panel, absorbed into the seams and cleats, and directed upward into the panels. It is the opposite of accumulated thermal movement.
- Accommodation of thermal movement occurs when hook strips, panel clips or cleats are used to hold sheet metal in place. Metal systems are most durable when they are able to float in at least one direction. Expansion joints also are used to minimize stresses and force caused by expansion and contraction.
- Accumulated thermal movement occurs when lengths of metal are mechanically attached to each other. For example, four 10-foot sections of metal that are riveted together will expand and contract exactly as a continuous 40-foot section of the same metal. The mechanical attachments will move with the metal as long as they do not penetrate the substrate.
- Fixed points secure metal to the structure of a house such as roof sheathing. Fasteners installed as fixed points direct the thermal movement of the metal away from the fastener but do not accommodate expansion and contraction in the manner cleats and hook strips do. Examples of fixed points include a fastener near the ridge of a standing-seam panel that penetrates the substrate or a downspout outlet in a built-in gutter system.
Who knew?
A ceremony was planned at The Gateway Arch in St. Louis for the morning of Oct. 28, 1965, to celebrate the topping out of the stainless-steel monument. Morning sunlight caused the arch to expand more than expected, and, as a result, the keystone was 5 inches too long to be set in place. Water was successfully sprayed on the south leg of the monument that morning to cool down the surface and cause it to contract.



